What comes to mind when you think about humidity? Sticky weather? Frizzy hair? While these are common associations, humidity is more than an inconvenience; it's a critical factor in various industries and applications.
Enter the humidity sensor, a small device with a big impact. But what exactly is a humidity sensor, and how does it work?
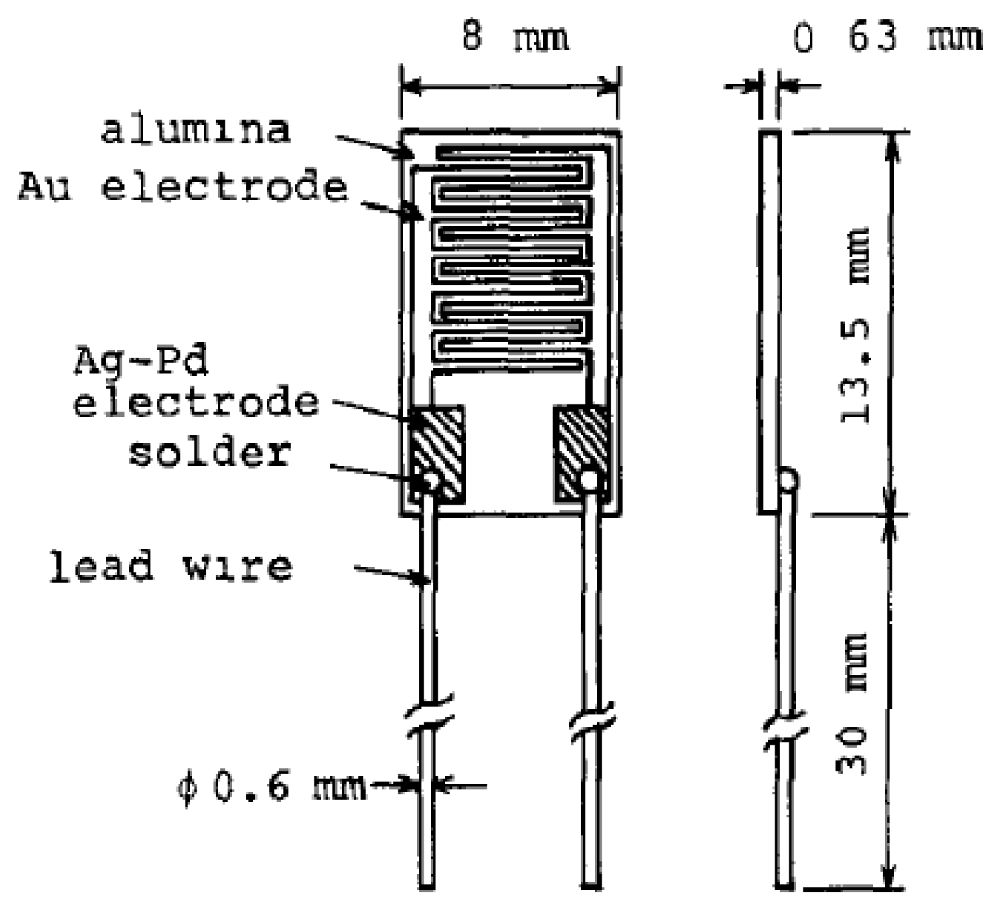
Let's explore their types, applications, and the science behind them.
How Humidity Sensors Work
Basic Principle
A humidity sensor fundamentally measures the moisture in the air. This reading of moisture can be expressed as either relative humidity (comparing the air moisture to its maximum capacity at a specific temperature) or absolute humidity (representing the total moisture content in the air irrespective of temperature).
Measuring Relative Humidity
Most humidity sensors function by assessing relative humidity levels. This is done by utilizing materials that modify their electrical traits, such as capacitance or resistance in response to changes in moisture levels. By detecting these alterations, the sensor can precisely determine relative humidity levels.
Measuring Absolute Humidity
Instruments that measure absolute humidity gauge the water vapor mass in a defined air volume. These sensors play a critical role in scenarios demanding accurate moisture levels, including scientific studies and specialized industrial operations.
Types of Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors come in various types, each with its working principles and applications.
Capacitive Humidity Sensors
Working Principle
Capacitive humidity sensors work by incorporating a thin film of polymer or metal oxide situated between two conductive plates.
The alteration in moisture content in the air results in a modification in the films dielectric constant subsequently affecting the capacitance measurement.
This change in capacitance is then quantified and transformed into a precise humidity reading.
Applications
These sensors find extensive applications in HVAC systems weather stations and various industrial settings due to their exceptional accuracy and reliability.
Resistive Humidity Sensors
Working Principle
Resistive humidity sensors use a hygroscopic (moisture-absorbing) material that changes its resistance as the humidity changes. The sensor measures this change in resistance to determine the humidity level.
Applications
Commonly found in household appliances, automotive applications, and environmental monitoring systems, these sensors are valued for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Thermal Conductivity Humidity Sensors
Working Principle
These sensors measure the thermal conductivity of the air, which changes with humidity. A thermistor (a type of resistor whose resistance varies with temperature) is used to measure this change, providing an accurate humidity reading.
Applications
They are often used in industrial drying processes, meteorological instruments, and HVAC systems.
Optical Humidity Sensors
Working Principle
Optical humidity sensors use light to measure humidity. They typically involve a light source and a detector, with the humidity level affecting the absorption or reflection of the light. This change is measured and converted into a humidity reading.
Applications
These sensors are used in high-precision applications such as laboratory instruments, environmental monitoring, and certain industrial processes.
Applications of Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors play a vital role in a wide range of applications across various industries.
Industrial Applications
Manufacturing Processes
In manufacturing, controlling humidity is crucial for maintaining product quality and consistency. Humidity sensors help ensure that the environment remains within specified limits.
Food Industry
Humidity control is essential in the food industry to prevent spoilage, maintain product quality, and ensure food safety. Sensors monitor and control humidity levels in storage and processing areas.
Agricultural Applications
Greenhouse Control
In agriculture, especially in greenhouses, maintaining the right humidity levels is vital for plant health and growth. Humidity sensors help automate and optimize these conditions.
Soil Moisture Monitoring
While not directly measuring air humidity, soil moisture sensors often work alongside humidity sensors to provide comprehensive data for irrigation management and crop health monitoring.
Healthcare Applications
Medical Equipment
Many medical devices require precise humidity control to function correctly. Humidity sensors ensure that these devices operate within the specified conditions.
Patient Monitoring
Humidity sensors are also used in patient monitoring systems to maintain a comfortable and healthy environment for patients, particularly in respiratory care.
Home and Office Applications
HVAC Systems
In homes and offices, HVAC systems use humidity sensors to maintain comfortable indoor conditions and improve energy efficiency.
Smart Home Devices
With the rise of smart homes, humidity sensors are now integrated into devices like smart thermostats and air quality monitors, providing users with better control over their living environments.
Meteorological Applications
Weather Forecasting
Humidity sensors are a key component of weather stations, providing data that helps meteorologists predict weather patterns and issue accurate forecasts.
Climate Research
In climate research, humidity sensors provide valuable data that helps scientists understand and model climate change and its impacts.
Advantages of Using Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors offer several advantages, making them indispensable in many applications.
Accuracy
Modern humidity sensors provide highly accurate readings, essential for processes where precise humidity control is critical.
Cost-effectiveness
Many humidity sensors are relatively inexpensive, making them accessible for a wide range of applications.
Durability
Humidity sensors are designed to withstand harsh conditions, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
Humidity Sensors Care
Despite their benefits, humidity sensors also face some challenges and limitations.
Calibration Issues
Humidity sensors need regular calibration to maintain their accuracy, which can be time-consuming and require specialized equipment.
Environmental Factors
Extreme temperatures, dust, and other environmental factors can affect the performance of humidity sensors, necessitating protective measures.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is required to ensure the sensors remain in good working condition, which can add to the operational costs.
What is New with Humidity Sensors?
The field of humidity sensing technology is continuously evolving, with exciting trends on the horizon.
Advances in Sensor Technology
New materials and technologies are being developed to improve the accuracy, reliability, and responsiveness of humidity sensors.
Integration with IoT
The integration of humidity sensors with the Internet of Things (IoT) is enabling more sophisticated and automated control systems, enhancing efficiency and convenience.
Enhanced Accuracy and Miniaturization
Future humidity sensors will likely be smaller and more accurate, making them suitable for an even wider range of applications.
Why AIM Dynamics is the Best for Humidity Sensors
AIM Dynamics stands out as a top choice when purchasing a humidity sensor. We offer many high-quality sensors to meet diverse needs, from home automation to industrial applications.
Our sensors are known for their accuracy, reliability, and durability, ensuring you get precise measurements every time.
AIM Dynamics also provides exceptional customer support, helping you choose the right sensor and offering guidance on installation and maintenance.
With our competitive pricing and commitment to quality, AIM Dynamics is your go-to source for the best humidity sensors on the market.
FAQs
What is the difference between relative and absolute humidity?
Relative humidity measures the amount of moisture in the air relative to the maximum amount it can hold at a given temperature, while absolute humidity measures the total amount of moisture in the air, regardless of temperature.
How do humidity sensors contribute to energy efficiency?
By providing accurate humidity readings, sensors enable HVAC systems and other devices to optimize their operation, reducing energy consumption and improving efficiency.
Can humidity sensors be used outdoors?
Yes, many humidity sensors are designed to withstand outdoor conditions and are used in applications such as weather stations and environmental monitoring.
What maintenance do humidity sensors require?
Humidity sensors typically require regular calibration and occasional cleaning to maintain their accuracy and performance.
Are there any emerging technologies in humidity sensing?
Yes, advances in materials and sensor technologies, as well as the integration with IoT, are driving the development of more accurate, reliable, and versatile humidity sensors.
Final Words
Humidity sensors are essential tools in various fields, from industrial processes to home comfort. By understanding how they work, the different types available, and their numerous applications, we can better appreciate the importance of these small yet powerful devices.
You Might Also Like: Integrating Modern and Traditional CNC Machines Using Wireless Router Technology








