Local Area Network
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network of interconnected computers and devices that covers a relatively small geographic area, such as a home, office, or campus. LANs are designed to facilitate the sharing of resources and information among connected devices, making it easier for users to communicate, collaborate, and access shared resources.
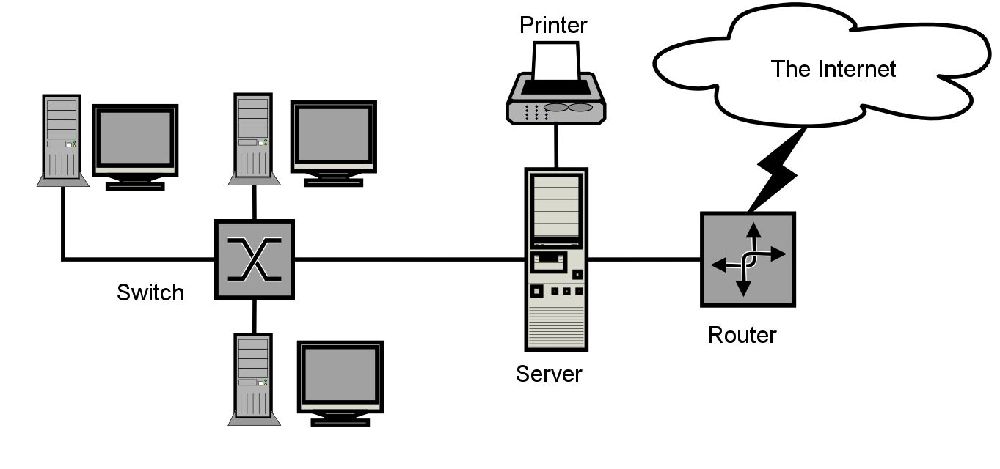
Here are some key features, uses, comparisons, industry applications, and frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to LANs:
Features of LAN:
- Geographical Scope: LANs are limited to a small geographic area, typically within a single building or a group of nearby buildings.
- High Data Transfer Rates: LANs offer high-speed data transmission, allowing for efficient communication and data sharing between devices.
- Private Ownership: LANs are usually owned, operated, and maintained by a single organization, making them private networks.
- Topologies: LANs can use various topologies, such as bus, star, ring, or mesh, to interconnect devices.
- Wired or Wireless: LANs can be implemented using wired technologies (e.g., Ethernet) or wireless technologies (e.g., Wi-Fi).
- Protocols: LANs use specific communication protocols, such as Ethernet and TCP/IP, to enable data exchange.
Uses of LAN:
- File Sharing: LANs enable users to share files and resources (e.g., printers) within the network.
- Communication: LANs facilitate instant messaging, email, and other forms of communication among users.
- Internet Access: LANs provide shared access to the internet, often via a router or gateway device.
- Resource Sharing: LANs allow multiple users to share resources like printers and storage devices.
- Collaboration: LANs support collaborative tools and applications for teamwork and data sharing.
- Gaming: LANs are commonly used for multiplayer gaming, where players connect their devices for real-time gaming experiences.
Comparison with Other Network Types:
- LAN vs. WAN (Wide Area Network): LANs cover a small area, while WANs connect larger geographic areas, often across cities, countries, or globally.
- LAN vs. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): LANs are smaller than MANs, which typically cover a city or metropolitan region.
- LAN vs. WLAN (Wireless LAN): LANs can be wired or wireless, with WLANs relying on wireless technology like Wi-Fi.
Industry Uses of LAN:
- Businesses: LANs are widely used in offices to connect computers, printers, and servers, improving productivity and resource sharing.
- Education: Educational institutions use LANs to provide internet access, share educational resources, and manage student data.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics use LANs for patient records, communication, and medical device integration.
- Manufacturing: LANs support automation, control systems, and data exchange in manufacturing plants.
- Entertainment: LANs are essential for gaming, streaming, and smart home devices.
FAQs:
1) What is the maximum distance a LAN can cover?
The maximum distance of a LAN depends on the technology used. Ethernet LANs typically have a range of up to 100 meters, while wireless LANs can cover a larger area but are subject to signal strength and interference.
2) What are common LAN protocols?
Common LAN protocols include Ethernet, Wi-Fi (for wireless LANs), and TCP/IP for data transmission.
3) Can I set up a LAN at home?
Yes, you can set up a LAN at home using a router and Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi. This allows you to connect your devices and share resources within your household.
4) What security measures should I take for my LAN?
Implement security measures such as password protection, firewalls, encryption, and regular updates to protect your LAN from unauthorized access and threats.
5) What is the future of LAN technology?
LAN technology continues to evolve, with advancements in higher data speeds, improved security, and increased support for IoT (Internet of Things) devices. The future of LANs will likely involve even faster and more secure connections to support the growing demands of modern applications and devices.
Conclusion:
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a crucial and adaptable technology that serves a fundamental role in connecting devices within a limited geographical area, such as homes, offices, and campuses. LANs offer rapid data transfer, promoting efficient resource sharing and communication.
Their applications span across various industries, ranging from business and education to healthcare and entertainment. As LAN technology continues to advance, it remains an indispensable component of our interconnected world, supporting the growing demand for seamless device-to-device communication and collaboration.
You Might Also Like: What is a BNC Connector?








