How Does a Potentiometer Work
In the realm of electronics, the potentiometer often goes unnoticed despite playing a critically significant role. Whether you're an enthusiast, a student, or a professional in the field, comprehending the potentiometer is vital to mastering various electronic applications.
Now, let's an overview into the essence of the potentiometer and uncover its paramount importance in modern electronics.
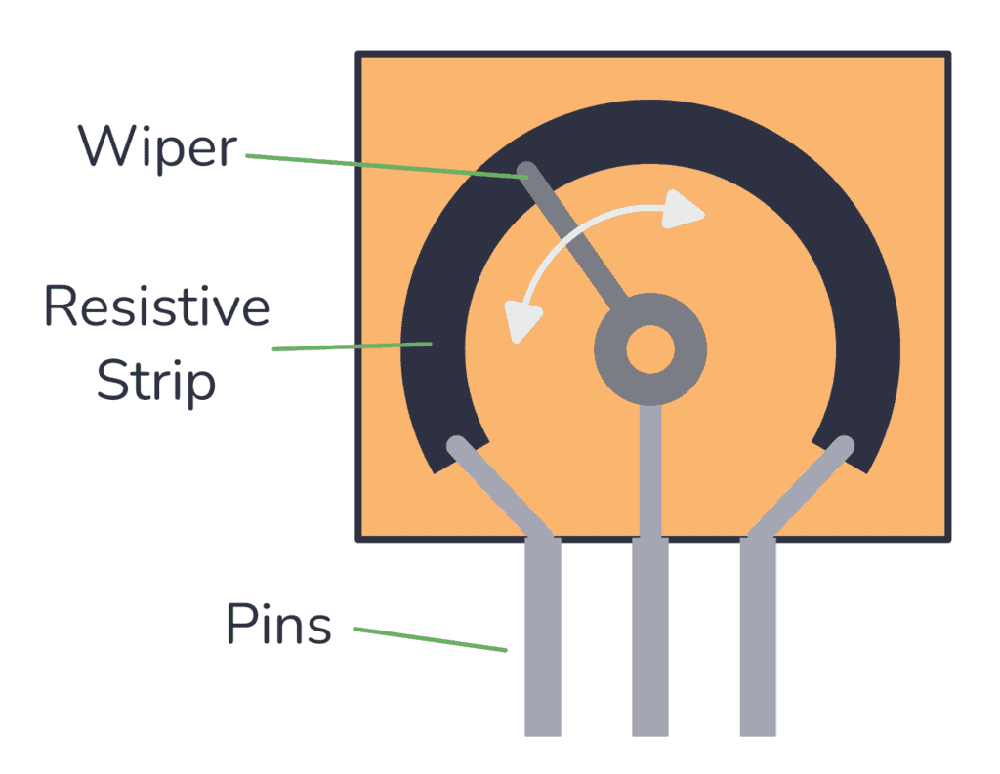
Potentiometer
A potentiometer, commonly known as a "pot," is a resistor with three terminals and a movable contact that can slide or rotate. It is a versatile component used in electrical circuits to measure and adjust the voltage difference or potential. Regulating the flow of electric current allows for precise control and customization.
Key Specifications of Potentiometers:
Specification | Description | Common Values |
Resistance Value | The electrical resistance offered by the pot. | 1 ohm to 1 megaohm |
Tolerance | The accuracy of the resistance value. | ±5%, ±10% |
Power Rating | The maximum power the pot can handle. | 0.1W to 0.5W |
Type | The design of the potentiometer (rotary/linear). | Rotary, Linear |
Types of Potentiometers
Rotary Potentiometer: The most common type used in volume control in audio systems.
Linear Potentiometer: Used where straight-line motion is involved, such as light dimmers.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Volume Controls: In audio equipment, pots adjust the volume by changing the resistance in the audio signal path.
Light Dimmers: Varying the resistance to control the brightness of lights.
Sensors are used as position sensors in joysticks and automotive throttle position sensors.
The Market Scenario: A Brief Overview
While specific statistics on potentiometers are not readily available, the global market for electronic components, including potentiometers, is projected to grow significantly. The expansion of consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and smart devices drives this.
How to Choose the Right Potentiometer
When selecting a potentiometer, consider:
Resistance Value and Tolerance: Match these to your circuit requirements.
Physical Size: Ensure it fits in your design.
Type: Rotary or linear, depending on the application.
Conclusion
Potentiometers, though simple, are incredibly versatile and essential in electronics. From adjusting your stereo's volume to controlling the speed of a motor, these components are the unsung heroes of the electronic world. As technology evolves, the applications of potentiometers continue to expand, making them a fundamental topic for anyone interested in electronics.
You Might Also Like: SIT1602BC-22-XXN-28.636300